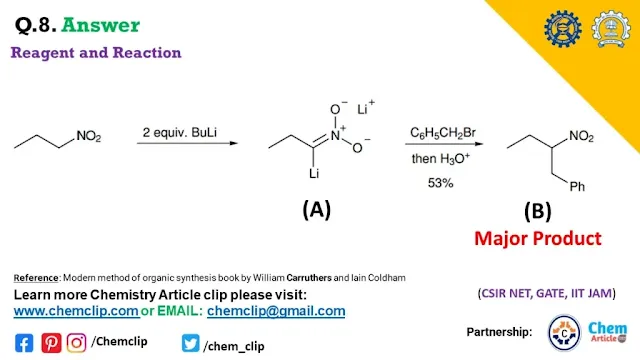
We have to discuss Butyl Lithium reacting with Nitroalkane. In presence of two equivalents of BuLi nitroalkane produced the dianion. Which is react with benzyl halide (e.g- PhCH2Br) formation of Carbon-Carbon signal bond in the alpha position of dianion.
Problem-solve:
The Reagents and reaction mechanism questions-answer for any entrance level exam preparation. Students and Master of chemical science who are practice the question solution series. First of all, try to think of the right approach: solve the question very easy way.
Q.8. The Major product B form Following the reaction: where A is intermediate of this reaction. Predict the product A and B with the proper mechanism.
Answer:
In this case, the use of two equivalents of butyllithium for produced of dianions. The dianions give products in good yield.
All reaction mechanisms are the same as discussed in the previous article or questions. The question is almost identical: replaced the carbonyl compound with a nitro-group containing the compound.
Reaction mechanism:
- Butyllithium act as a base which is abstract the most acidic proton in nitroalkanes. the more acidic protons are mentioned in the alpha position of the given nitro compound. and formation of the dianion.
- The dianion (like enolate) acts as a nucleophile and attaches to benzyl halide. That is on type Nucleophilic substitution reaction. Where release the Bromium ions.
- This process goes through strong work up in H3O+.
- Produced the product with a (carbon-carbon signal bond formation) good yield.
Reference:
Modern organic synthesis by Carruthers Book. Chapter: Carbon-Carbon Singal Bond formation. In part of Organolithium catalysts or reagents react with a carbonyl compound: ketone, ester, aldehyde, etc. Correspond to Nitroalkynes (Nitro group contain compound) react with organolithium reagents (BuLi).
Follow our official Facebook page: @chemclip or Twitter handle: @chem_clip